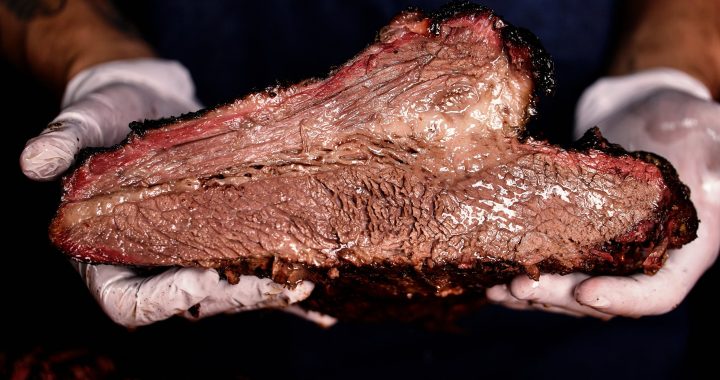
Lab meat will be the food for astronauts going to Mars
3 min read
In the 2030s, the first humans must cross space and reach Mars, in a mission expected to last about two years. In order to be realized, many challenges still have to be overcome, such as the issue of food. Experts say it must be pointless to eat all the prepared foods, which would force the astronauts to produce their own food. In this limited menu there is an option Lab grown meat.
To make the production of meat grown in microgravity environments possible, the European Space Agency (ESA)ESA), Thursday (31), Supporting new research in the region. “Traditional production of food of animal origin, such as meat, in space is unimaginable,” says Paolo Corradi, an engineer at the European Space Agency, of the importance of such initiatives.

In the whirlwind of new research that seeks to nourish astronauts and take care of their health on long spaceflights, researchers at the University of California, USA, are studying how to make a genetically modified lettuce farm, for example, available. The idea is that the vegetable acts as a kind of medicine and reduces the impact of bone loss caused by microgravity on the crew..
Want to stay up to date with the best tech news of the day? Access and subscribe to our new YouTube channel, Canaltech News. Every day a summary of the most important news from the world of technology for you!
If the initiatives are successful, new technologies must also be applied to the Earth, and most likely will lead to numerous benefits for Earth’s inhabitants.
Long Distance Travel Challenge: Food
“For human long-term exploration missions far from Earth, we’ll need to move a lot of long-lived food,” says engineer Corradi. On the other hand, there is a risk of food deterioration or even loss, “which would greatly limit the degree of self-sustainability and mission resilience” on a distant planet, he adds.
“Therefore, if we are to be successful in long-range human exploration far from Earth, we need to rethink our current approach to feeding astronauts and providing the means to efficiently produce food on board,” Corradi confirms.
Studies of meat cultivation
Currently, experiments with space-grown meat are just beginning. On the innovation radar, ESA should allocate financial resources to the following two groups:
- Partnership between the German Yuri Gravity and the University of Reutlingen;
- Partnership between British companies Kayser Space, Cellular Agriculture and Campden BRI.
What would the search process look like?
According to Engineer Corradi, the research to develop safe and nutritious cultured meat should involve several steps. Initially, you will analyze the difference and compare the nutritional value and potential benefits of the grown products. That’s because new alternatives have to be as protein and nutritious as the options on Earth.

After the analysis, Corradi explains that the groups should establish “a set of requirements for growing meat in space” and “dietary guidelines for astronauts and future human space missions.” The definitions then have to be shared with the Space Medicine Group and other ESA researchers.
“Finally, the teams will provide a preliminary design of the cultured meat production system for space applications, assess its feasibility and analyze its performance,” says Paolo. In addition, they should submit a study of the potential commercial utility of the initiative’s terrestrial applications.
In the future, cultured meat may make conventional meat something “old”, but research and testing is still needed to enable the next generation of food that will be consumed by astronauts, and most likely Earthlings.
source: ESA

“Entrepreneur. Music enthusiast. Lifelong communicator. General coffee aficionado. Internet scholar.”

:strip_icc()/s04.video.glbimg.com/x720/11792055.jpg)

:strip_icc()/s03.video.glbimg.com/x720/11786998.jpg)