NASA Spotlight: The Great Tarantula Nebula is the astronomical picture for today
2 min read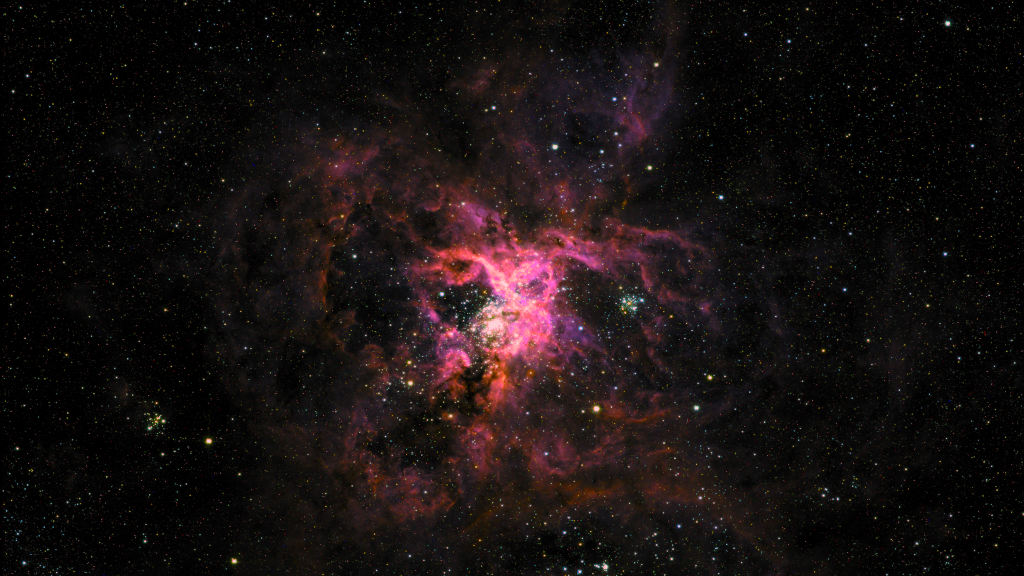
The Tarantula Nebula is visible in an astronomical image released by NASA on Thursday (27). Also known as “30 Doradus,” it is more than a thousand light-years in diameter and is located within the Large Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way.
Located about 160 light-years away from us, this nebula is considered one of the largest and most violent star-forming regions in the Milky Way. This “cosmic spider” can be found in the center of the image below, captured by the SuperBIT telescope:
The nebula’s structure was shaped by intense radiation, stellar winds and shocks from supernova explosions from R136, a young cluster of massive stars within it. The stars there are responsible for both the glowing energy of the nebula and its filaments.
Despite being the highlight of the image, don’t think the tarantula is alone: It’s surrounded by star-forming regions full of young star clusters, filamentous structures, and bubble clouds.
Facts about the Tarantula Nebula
How about learning more about the secrets of the Tarantula Nebula? This cloud can be found in the sky of the Southern Hemisphere and can be seen with the naked eye, and appears as a large, milky-like formation.
By the way, it is not for nothing that the Tarantula is considered the largest star nursery in the local universe: if such a large complex of stars, gas and dust were at the same distance from us as the Orion Nebula, then it would be visible during the day and would cover 25% of the sky.
Not only did intensive processes take place inside it. While orbiting the Milky Way, this nebula appears to have interacted with our galaxy, and these rings have resulted in active star formation processes.
source: APOD

“Entrepreneur. Music enthusiast. Lifelong communicator. General coffee aficionado. Internet scholar.”

:strip_icc()/s04.video.glbimg.com/x720/11792055.jpg)

:strip_icc()/s03.video.glbimg.com/x720/11786998.jpg)